Teach Corrective Mathematics
-
Module Introduction5 Topics
-
Overview14 Topics|2 Tests
-
Cover
-
Lesson Objective
-
Opening the Lesson
-
Direct Instruction Overview
-
Corrective Mathematics Training
-
Core Features of Corrective Mathematics
-
Video: Corrective Mathematics in Action
-
Program Students and Time Commitments
-
Check Your Understanding
-
Corrective Mathematics Teacher and Student Materials
-
Teach Tracks and Concepts
-
Test Your Understanding
-
Review
-
Lesson Completed
-
Cover
-
Setting Up for Success and Teaching Strategies25 Topics|4 Tests
-
Cover
-
Lesson Objective
-
Opening the Lesson
-
Placement Testing: Two Methods
-
Placement Test Guidelines
-
Placement Test Directions
-
Placement Criteria
-
Check Your Understanding
-
Video: Placement Test
-
Classroom Arrangement
-
Video: Classroom Arrangement and Active Monitoring
-
Using a Script
-
Signals
-
Types of Signals
-
Pacing
-
Check your understanding
-
Video: Teaching Strategies for Effective Teaching: Use of Script, Signals and Pacing
-
Corrections
-
General Correction Procedures
-
Specific Correction Procedures
-
Video: General and Specific Correction Procedures
-
Check Your Understanding
-
Test Your Understanding
-
Review
-
Lesson Completed
-
Cover
-
Tracks in Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication and Division Modules25 Topics|4 Tests
-
Cover
-
Lesson Objective
-
Opening the Lesson
-
Overview of Tracks
-
Facts Track
-
Fact Track: Number Families in the Addition and Subtraction Modules
-
Video: Addition and Multiplication Fact Track Number Families
-
Practise Number Families Facts from the Division Module Lesson
-
Fact Track Fact Series
-
Special Facts
-
Correcting Errors Procedures
-
Video: Fact Tracks with Error Correction Procedures
-
Check Your Understanding
-
Operation Track
-
Video: Preskills to Operations
-
Teaching Tracks and Corrections Tips
-
Check your understanding
-
Story Problem Track
-
Place Value Track
-
Correction and Mastery
-
Video: Error Correction Procedure
-
Check Your Understanding
-
Test Your Understanding
-
Review
-
Lesson Completed!
-
Cover
-
Skills in Basic Fractions, Fractions, Decimals and Percents, Ratios and Equations21 Topics|3 Tests
-
Cover
-
Lesson Objective
-
Opening the Lesson
-
Overview
-
Basic Fractions
-
Basic Fractions Components
-
Teaching Tips for Basic Fractions
-
Video: Exercise 2, Lesson 27 of Multiplication Module
-
Check Your Understanding
-
Errors Correction
-
Video: Error Correction in Basic Fractions Problems
-
Fractions, Decimals, and Percents
-
Ratios and Equations
-
Check Your Understanding
-
Process Error Correction Procedure for Fractions and Ratios and Equations
-
Video: Lesson 5, Exercise 3 from Ratios and Equations Module
-
Teaching Tips for Advanced Fractions Skills
-
Practice Lesson
-
Test Your Understanding
-
Review
-
Lesson Completed
-
Cover
-
Teacher Practice Formats and Individual Turns19 Topics|3 Tests
-
Cover
-
Lesson Objective
-
Opening the Lesson
-
Teacher Practice Formats
-
Facts Formats
-
Operations Formats
-
Video: Lesson 2, Exercise 4: Fact Number Families Format
-
Individual Turns
-
Check Your Understanding
-
Error Corrections
-
Video: Lesson 30, Exercise 5 Teaching Format
-
Story Problem Formats
-
Naming Problem Format
-
Practise Format
-
Check Your Understanding
-
Teaching to Mastery
-
Test Your Understanding
-
Review
-
Lesson Completed!
-
Cover
-
Fact Games, Timing formats, and Fact Mastery Test17 Topics|3 Tests
-
Cover
-
Lesson Objective
-
Opening the Lesson
-
Fact Practice
-
The Fact Game and Its Procedure
-
Video: Administering Fact Game
-
Fact Game Monitoring and Work Check
-
Video: Fact Game Check Procedure
-
Check Your Understanding
-
Timing Format and Its Procedures
-
Video: Administering Timing Format
-
Fact Mastery Tests and Their Procedures
-
Video: Fact Mastery Test Preparation Procedure
-
Check Your Understanding
-
Test Your Understanding
-
Review
-
Lesson Completed!
-
Cover
-
Worksheets, Independent Work and Work Checks20 Topics|3 Tests
-
Cover
-
Lesson Objective
-
Opening the lesson
-
Worksheets
-
Diagnosing Worksheet Errors
-
Video: Administering Worksheets
-
Facts Errors in Worksheets
-
Process Errors in Worksheets
-
Video: Diagnosis of a Worksheet Error and Its Correction
-
Story Problem Errors in Worksheets
-
Video: Story Problem’s Process Error Corrections
-
Check Your Understanding
-
Workchecks
-
Individual Workcheck
-
Peer Workcheck
-
Video: Administering Workchecks
-
Check Your Understanding
-
Test Your Understanding
-
Review
-
Lesson Completed!
-
Cover
-
Mastery Tests and Five Lesson Point Graph21 Topics|3 Tests
-
Cover
-
Lesson Objective
-
Opening the Lesson
-
Mastery Tests Overview
-
Mastery Tests and Their Procedures
-
Video: Administering a Mastery Test
-
Remediation Directions
-
Error Types and Correction Methods
-
Check Your Understanding
-
Progressing at an Optimal Rate
-
Cumulative Reviews and Review Lessons
-
Point System Overview
-
The Point Summary Charts
-
Video: Awarding Points Procedure
-
Five-Lesson Point Graph
-
Recording Daily Points
-
Video: Recording Daily Points
-
Check Your Understanding
-
Test Your Understanding
-
Review
-
Lesson Completed
-
Cover
-
Setting Expectations and Motivating Students27 Topics|4 Tests
-
Cover
-
Lesson Objective
-
Opening the Lesson
-
Setting Expectations and Motivating Students: Overview
-
Placement Seating and STAR Rule
-
Video: Setting Expectations and Motivating Students
-
Addressing Students’ Concerns
-
Establishing Rules for Corrective Mathematics
-
Check Your Understanding
-
Teaching to Criterion
-
Teacher Self-Evaluation
-
Video: Teacher Self-Evaluation
-
Lesson Preparation and Motivation
-
Transition and Monitoring
-
Video: Transition and Monitoring
-
Check Your Understanding
-
General Motivation
-
Using Affirmations to Motivate Students
-
Specific Positive Praise
-
Video: Teaching Using Affirmations and Specific Positive Praise
-
Teacher–Student Game
-
Rewards and Celebrations
-
Video: Teacher-Student Game and Reward and Celebrations
-
Check Your Understanding
-
Test Your Understanding
-
Review
-
Lesson Completed
-
Cover
-
Teaching a Lesson from Corrective Mathematics24 Topics|3 Tests
-
Cover
-
Lesson Objective
-
Opening the Lesson
-
Lesson 42, Exercise 1: Facts: Introducing Five Facts in Series
-
Lesson 42, Exercise 2: Place Value: Practise Putting Commas
-
Signals
-
Lesson 42, Exercise 3: Operations: Which Box is Carry to
-
Video: Demonstration of Exercises 1–3 of Lesson 42
-
Lesson 42, Exercise 4: Facts: Practising Carrying and Non-carrying Additional Pre-skills
-
Lesson 42, Exercise 5: Timing Format
-
Video: Timing Format
-
Check Your Understanding
-
Lesson 42, Exercise 6: Facts: Practising Commutative Property
-
Lesson 42, Exercise 7: Introducing Subtraction Problems
-
Video: Introducing Subtraction Problems with Error Correction
-
Lesson 42: Exercise 8: Preparation for Mastery Test
-
Lesson 42: Exercise 9 Independent Work
-
Check Your Understanding
-
Lesson 42, Exercise 10: Workcheck
-
Lesson 42, Exercise 11: Fact Game
-
Video: Fact Game and Points Calculation and Point Summary Chart Fill
-
Test Your Understanding
-
Review
-
Lesson Completed
-
Cover
-
Module evaluation survey1 Topic
Participants 13

Special Facts
In Corrective Mathematics, some facts are referred to as Special Facts. They are given more time and practice for students to master the skill.
“Division Remainder Facts” are one of the special facts that is given attention in Corrective Mathematics lessons. Students are taught divisions with varying facts to help them understand the concept of the remainder.

For example, in the display below, students are taught that 5 can be divided into numbers 31 to 34, 6 times, which results in a remainder each time.
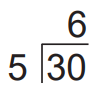
Teaching problems as “facts” is another type of special fact that is given time and practice in Corrective Mathematics. In the example displayed below, students learn to compute answers silently by applying the learned skill – for example, the remainder skill – to find solutions to many addition and multiplication problems.